MongoDB HA Test with Pymongo
by Peng Xiao
1 Environment Setup
One CentOS 7 machine
$ more /etc/redhat-release
CentOS Linux release 7.2.1511 (Core)
Mongodb version
$ mongod --version
db version v3.2.6
git version: 05552b562c7a0b3143a729aaa0838e558dc49b25
OpenSSL version: OpenSSL 1.0.1e-fips 11 Feb 2013
allocator: tcmalloc
modules: none
build environment:
distmod: rhel70
distarch: x86_64
target_arch: x86_64
Pymongo version
>>> import pymongo
>>> pymongo.version
'3.2'
>>>
1.1 Install mongodb
Please see https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/tutorial/install-mongodb-on-red-hat/
1.2 Configure mongodb
We will configure three nodes replication in one machine,like:
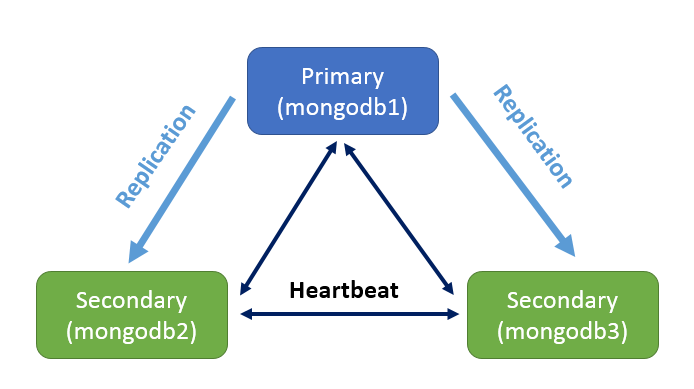
1) Prepare three mongodb config file
$ ls /etc/ | grep mongo
mongod1.conf
mongod2.conf
mongod3.conf
Each config file is:
$ more /etc/mongod1.conf
# mongod.conf
systemLog:
destination: file
logAppend: true
path: /var/log/mongodb1/mongod.log
storage:
dbPath: /var/lib/mongo1
journal:
enabled: true
processManagement:
fork: true # fork and run in background
pidFilePath: /var/run/mongodb1/mongod.pid # location of pidfile
net:
port: 27017
replication:
replSetName: rs0
$ more /etc/mongod2.conf
# mongod.conf
systemLog:
destination: file
logAppend: true
path: /var/log/mongodb2/mongod.log
storage:
dbPath: /var/lib/mongo2
journal:
enabled: true
processManagement:
fork: true # fork and run in background
pidFilePath: /var/run/mongodb2/mongod.pid # location of pidfile
net:
port: 27018
replication:
replSetName: rs0
$ more /etc/mongod3.conf
# mongod.conf
systemLog:
destination: file
logAppend: true
path: /var/log/mongodb3/mongod.log
storage:
dbPath: /var/lib/mongo3
journal:
enabled: true
processManagement:
fork: true # fork and run in background
pidFilePath: /var/run/mongodb3/mongod.pid # location of pidfile
net:
port: 27019
replication:
replSetName: rs0
1.3 Start 3 mongodb instances and init them
$ sudo /usr/bin/mongod -f /etc/mongod1.conf
$ sudo /usr/bin/mongod -f /etc/mongod2.conf
$ sudo /usr/bin/mongod -f /etc/mongod3.conf
Connect to one of your mongod instances through the mongo shell. MongoDB initiates a set that consists of the current member and that uses the default replica set configuration.
1.4 Add the remaining members to the replica set.
rs.add("127.0.0.1:27018")
rs.add("127.0.0.1:27019")
through rs.status we can see the status of the replica set
rs0:PRIMARY> rs.status()
{
"set" : "rs0",
"date" : ISODate("2016-05-22T04:45:22.195Z"),
"myState" : 1,
"term" : NumberLong(3),
"heartbeatIntervalMillis" : NumberLong(2000),
"members" : [
{
"_id" : 0,
"name" : "127.0.0.1:27017",
"health" : 1,
"state" : 1,
"stateStr" : "PRIMARY",
"uptime" : 166805,
"optime" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1463737764, 8),
"t" : NumberLong(3)
},
"optimeDate" : ISODate("2016-05-20T09:49:24Z"),
"electionTime" : Timestamp(1463725527, 1),
"electionDate" : ISODate("2016-05-20T06:25:27Z"),
"configVersion" : 3,
"self" : true
},
{
"_id" : 1,
"name" : "127.0.0.1:27018",
"health" : 1,
"state" : 2,
"stateStr" : "SECONDARY",
"uptime" : 166799,
"optime" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1463737764, 8),
"t" : NumberLong(3)
},
"optimeDate" : ISODate("2016-05-20T09:49:24Z"),
"lastHeartbeat" : ISODate("2016-05-22T04:45:20.570Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv" : ISODate("2016-05-22T04:45:20.570Z"),
"pingMs" : NumberLong(0),
"syncingTo" : "127.0.0.1:27019",
"configVersion" : 3
},
{
"_id" : 2,
"name" : "127.0.0.1:27019",
"health" : 1,
"state" : 2,
"stateStr" : "SECONDARY",
"uptime" : 166794,
"optime" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1463737764, 8),
"t" : NumberLong(3)
},
"optimeDate" : ISODate("2016-05-20T09:49:24Z"),
"lastHeartbeat" : ISODate("2016-05-22T04:45:21.356Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv" : ISODate("2016-05-22T04:45:21.356Z"),
"pingMs" : NumberLong(0),
"syncingTo" : "127.0.0.1:27017",
"configVersion" : 3
}
],
"ok" : 1
}
rs0:PRIMARY>
1.5 Add authentication
1) Create the keyfile your deployment will use to authenticate to members to each other.
$ openssl rand -base64 741 > /home/mongodb/mongodb-keyfile
$ chmod 600 mongodb-keyfile
2)Enable authentication for each member of the sharded cluster or replica set.
In each replica member’s configure file, please add this:
security:
keyFile: /home/mongodb/mongodb-keyfile
If the replica members are in different machines, Pleas copy the key file to the host machine where the replica member located in.
3) Create user administrator
use admin
db.createUser(
{
user: "myUserAdmin",
pwd: "abc123",
roles: [ { role: "userAdminAnyDatabase", db: "admin" } ]
}
)
4) Restart all mongodb instances
$ mongo
MongoDB shell version: 3.2.6
connecting to: test
rs0:PRIMARY> rs.status()
{
"ok" : 0,
"errmsg" : "not authorized on admin to execute command { replSetGetStatus: 1.0 }",
"code" : 13
}
rs0:PRIMARY> use admin
switched to db admin
rs0:PRIMARY> db.auth("myUserAdmin","abc123")
1
2 Testing
2.1 Test case 1: Basic operations
We use pymongo to do some basic testing.
Connecting to a Replica Set
>>> from pymongo import MongoClient
>>> MongoClient("10.75.44.10", replicaset='rs1')
MongoClient([u'mongodb2:27017', u'mongodb1:27017', u'mongodb3:27017'])
>>>
Write operation:
>>> from pymongo import MongoClient
>>> db = MongoClient("127.0.0.1", replicaset='rs1').demo
>>> db
Database(MongoClient([u'mongodb2:27017', u'mongodb1:27017', u'mongodb3:27017']), u'demo')
>>> db.connection.host
'10.75.44.10'
>>> db.connection.port
27017
>>>
看到目前对于数据库的操作是PRIMARY,也就是host mongodb1。 然后对数据库写入一条record:
>>> db.test.insert({'x':1})
ObjectId('54b8b1a1c77b3b3b354869a3')
>>> db.test.find_one()
{u'x': 1, u'_id': ObjectId('54b8b1a1c77b3b3b354869a3')}
>>>
此时,把mongodb1的mongod stop掉。
>>> db.test.find_one()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pymongo/collection.py", line 713, in find_one
for result in cursor.limit(-1):
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pymongo/cursor.py", line 1038, in next
if len(self.__data) or self._refresh():
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pymongo/cursor.py", line 982, in _refresh
self.__uuid_subtype))
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pymongo/cursor.py", line 906, in __send_message
res = client._send_message_with_response(message, **kwargs)
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pymongo/mongo_client.py", line 1186, in _send_message_with_response
sock_info = self.__socket(member)
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pymongo/mongo_client.py", line 913, in __socket
"%s %s" % (host_details, str(why)))
pymongo.errors.AutoReconnect: could not connect to 10.75.44.10:27017: [Errno 111] Connection refused
>>> db.test.find_one()
{u'x': 1, u'_id': ObjectId('54b8b1a1c77b3b3b354869a3')}
>>> db.connection.host
u'mongodb3'
>>> db.connection.port
27017
>>>
发现有个pymongo.errors.AutoReconnect的异常,不过马上恢复了,而且此时的操作数据库变成了mongodb3,也就是现在的PRIMARY.
如果需要从Secondary读取数据,可以设置ReadPreference.
>>> from pymongo.read_preferences import ReadPreference
>>> db.test.find_one()
{u'x': 1, u'_id': ObjectId('54b8b1a1c77b3b3b354869a3')}
>>> db.test.find_one(read_preference=ReadPreference.SECONDARY)
{u'x': 1, u'_id': ObjectId('54b8b1a1c77b3b3b354869a3')}
>>>
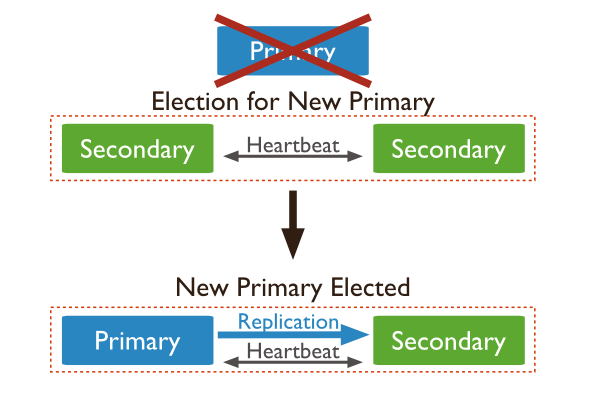
2.2 Test case 2: PRIMARY lost connection with all SECONDARY
假如PRIMARY和其它所有的SECONDARY失去联系了,那么PRIMARY就无法进行读写操作了。
>>> db.test.insert({'x':3})
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pymongo/collection.py", line 402, in insert
gen(), check_keys, self.uuid_subtype, client)
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pymongo/mongo_client.py", line 1125, in _send_message
raise AutoReconnect(str(e))
pymongo.errors.AutoReconnect: not master
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>> db.test.insert({'x':3})
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pymongo/collection.py", line 363, in insert
client._ensure_connected(True)
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pymongo/mongo_client.py", line 924, in _ensure_connected
self.__ensure_member()
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pymongo/mongo_client.py", line 797, in __ensure_member
member, nodes = self.__find_node()
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pymongo/mongo_client.py", line 888, in __find_node
raise AutoReconnect(', '.join(errors))
pymongo.errors.AutoReconnect: [Errno 111] Connection refused, [Errno 111] Connection refused, mongodb3:27017 is not primary or master
>>>
直到有至少两个Replica Set的host连接,然后选出新的PRIMARY。
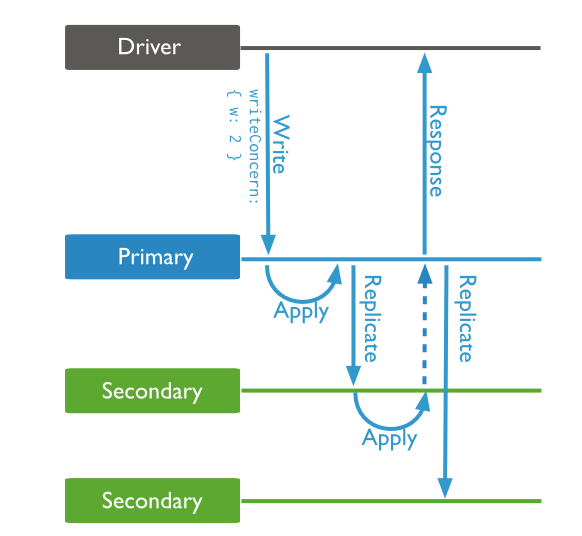
2.3 Test case 3: Write Concern
根据Write Concern for Replica Sets的介绍:
>>> db
Database(MongoClient([u'mongodb2:27017', u'mongodb1:27017', u'mongodb3:27017']), u'demo')
>>> db.write_concern
{}
>>> db.write_concern = {'w':2, 'wtimeout':5000}
>>> db.write_concern
{'wtimeout': 5000, 'w': 2}
>>> db.test.insert({'y':2})
ObjectId('54b8b89dc77b3b3b354869a4')
默认的write concern是空的配置。write concern有四个参数:w,wtimeout,j, fsync。
其中比较重要的是w和wtimeout。
w: (integer or string)If this is a replica set, write operations will block until they have been replicated to the specified
number or tagged set of servers. w=
wtimeout: (integer) Used in conjunction with w. Specify a value in milliseconds to control how long to wait for write
propagation to complete. If replication does not complete in the given timeframe, a timeout exception is raised.
Reference
Three Member Replica Sets from mongodb.org
http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/replication/
How to Setup MongoDB Replication Using Replica Set and Arbiters
Subscribe via RSS
